Content
- 1 Botanical description of dioecious nettle
- 2 Breeding methods for dioecious nettle
- 3 Growing features
- 4 The chemical composition of dioecious nettle
- 5 Medicinal properties of dioecious nettle
- 6 The use of dioecious nettle in medicine
- 7 Terms and rules for collecting dioecious nettle
- 8 The use of dioecious nettle in other areas
- 9 Conclusion
Stinging nettle is an ambiguous plant. She helps to heal diseases, during the wars she saved from hunger. Many people still use it in salads. But the gardeners hate her fiercely. And there are reasons for that. In summer cottages, it is an ineradicable and tenacious weed.
Botanical description of dioecious nettle
A perennial dioecious herb with a strong root system that develops horizontally. Depending on climatic conditions, it grows from 60 cm to 2 m in height. The Latin name for dioecious nettle is Urtica dioica. The specific name “dioicus” originates from the ancient Greek word meaning “two houses”, the generic name comes from the Latin word “uro”, that is, “burn”.
Stems are erect, fibrous, hollow inside. The cross section is tetrahedral. Originally single escape. Axillary stems develop over time. Stinging nettle is covered with stinging hairs.
The leaves of dioecious nettle are equilateral, opposite, simple. The color is dark green. The tops of the leaf blades are pointed. The edges are coarsely serrated or coarsely toothed. The shape is oblong, ovate-lanceolate or heart-shaped. Sometimes elliptical is found. The ratio of the length and width of the leaf blade is 2: 1. The bases of the leaves have a deep notch up to 5 mm. The petioles are long.
Inflorescences are drooping panicles. Peduncles are located at the base of the petioles. The lowest inflorescences appear at the height of the 7-14th node from the ground. Peduncles can also grow on axillary shoots. Dioeous plants can have only male or female flowers on one specimen. Because of this, half of the dioecious nettle population remains sterile.
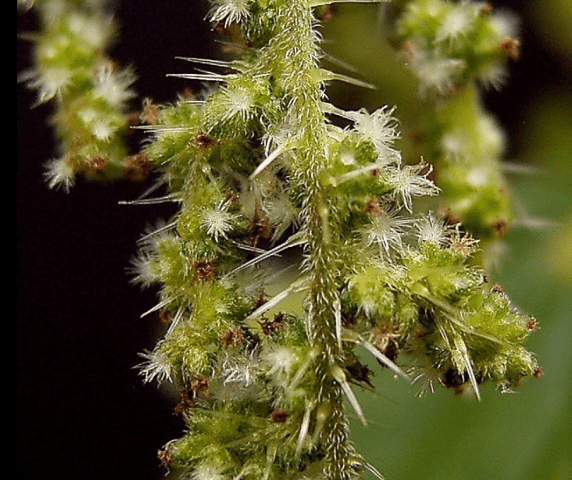

Unlike male flowers, female dioecious nettle inflorescences have protection
Fruits are small elliptical nuts 1-1.4 mm long. The color is yellowish or light brown. The surface is matt.
The root system of dioecious nettle is located horizontally and shallowly underground. Stolon-shaped roots grow 35-40 cm per year.
Defense mechanism against herbivores
All aerial parts of dioecious nettle are covered with dense, stinging hairs. The latter are one giant cell, similar to a medical ampoule and filled with silicon salts. The tip of the "ampoule" protrudes beyond the plant. The walls of the protective cell are very fragile. They break even with little impact. The sharp end of the hair pierces the skin, and the juice enters the herbivore's body, which is filled with the cell. Contents of the "ampoule":
- formic acid;
- histamine;
- choline.
These substances irritate the skin and cause a "burn" sensation.
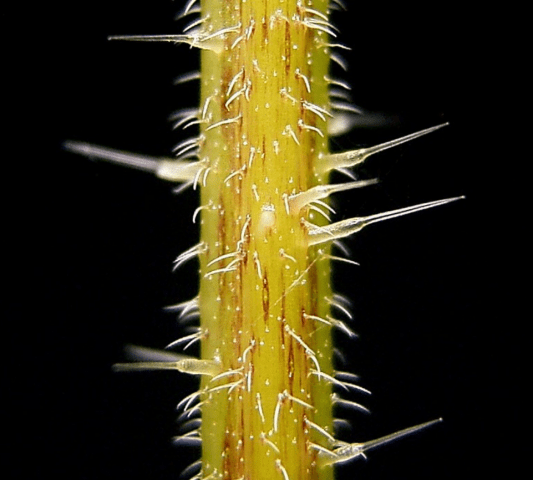

Some tropical nettles can be fatal
Where does dioecious nettle grow
The weed is very unpretentious and easily adapts to different climatic conditions. Distributed in the temperate climatic zone of the northern and southern hemispheres. The seeds were brought to the continents, where it was not originally, man. In this way, the plant penetrated into North America and Australia. In Eurasia, dioecious nettle grows not only in Europe. It can be found in Asia Minor and Western Asia and in India. In North Africa, its range stretches from Libya to Morocco. Only absent in South America.
In Russia, it is distributed in Western Siberia and the European part. Was introduced to the Far East and Eastern Siberia. In natural conditions, it prefers the forest and forest-steppe zone.
Stinging nettle is a ruderal plant. That is, she prefers:
- forest clearings;
- damp forests and meadows;
- ditches;
- ravines;
- garbage places near fences and dwellings;
- abandoned land;
- shores of reservoirs.
Due to its ability for vegetative reproduction, it forms "clean" thickets that do not have inclusions of extraneous flora over large areas.
Stinging nettle has no conservation status. On the contrary, it is considered a difficult weed to eradicate. But it is easy to confuse it with another nettle: Kiev. Both species are very similar:
- inflorescences;
- leaves;
- the height of the shoots.
The Kiev law really protects in some regions:
- Voronezh and Lipetsk regions;
- Belarus;
- Hungary;
- Czech Republic.
But if you look closely, it is not difficult to distinguish a protected species from a malicious weed.
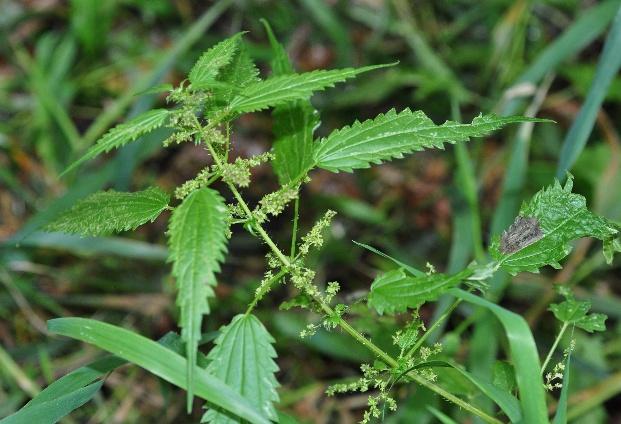

The main difference between Kiev and dioecious nettle is longer and narrower leaf blades.
Stinging nettle, wild or not
Stinging nettle was a cultivated plant until the 19th century, when it was grown for fiber for the textile industry. Today, gardeners are not happy with her appearance. If you give free rein to dioecious nettles, it will quickly fill all the space available to it. And getting rid of it is very difficult.
But although dioecious nettle has given way to cotton and synthetic fabrics, South Asian countries still use ramie / bommeria fibers, which are specially grown on an industrial scale. The Asiatic herb belongs to the same family as the dioecious nettle, but it has a different genus and no stinging hairs.

Bomeria fabrics are valued for their resemblance to natural silk
Is stinging nettle poisonous
It depends on the point of view. The stinging bristles contain poison that affects the skin and mucous membranes. But as a food plant, dioecious nettle is harmless. You just need to pour boiling water over it to avoid burns. The danger is the consumption of too many nettle leaves and seeds, due to the high content of vitamin K, which clotts the blood.
How to distinguish stinging nettle from stinging nettle
Stinging nettles and stinging nettles look very similar at a young age. But in mature plants, details become noticeable, by which it is easy to distinguish them from each other:
- the difference in the height of the shoots: stinging no more than 35 cm, dioecious - up to 2 m;
- the appearance of the inflorescence - in the burning spike, in the dioecious - a hanging panicle;
- inflorescence size: in dioecious, longer than petioles, in stinging ones, shorter or equal.
Burning, unlike dioecious, does not multiply with the help of the root system, therefore, it forms only small clumps, without pretending to all the available space.
The growing places of the stinging and dioecious are the same:
- vacant lots;
- vegetable gardens;
- road shoulders;
- along the edges of compost pits;
- spaces near houses and fences.
Main condition for growth: nitrogen-rich soil.

The stinging variety is used to treat KSD and to heal skin ulcers.
Breeding methods for dioecious nettle
Stinging nettle is propagated by seeds and roots. The germination capacity of nettle "nuts" is low. In addition, only female plants can produce fruits. This method is suitable for transferring future offspring over long distances. Seed germination may increase after passing through the digestive tract of cattle.
For the conquest of nearby spaces, the vegetative method is more effective, since male specimens can also produce clones. There are growth buds on the stolons, which are activated the next year. Thus, even a male plant can produce clones and invade the entire surrounding area.

Roots are the main breeding method for dioecious nettle
Growing features
They do not exist, since no one grows the weed on purpose. But if there is a desire to completely destroy your summer cottage, then you can make a well-manured bed. It is better to mix the soil with humus in a 1: 1 ratio. After that, pour out the seeds and lightly sprinkle them with earth. It is not necessary to embed it deeply. The soil is kept slightly moist. The illumination of the bed does not matter. With enough water and nutrients, stinging nettle grows well in the shade and sun.
The chemical composition of dioecious nettle
Young shoots of dioecious nettle contain:
- fiber - 37%;
- crude protein - 23%;
- ash - 18%;
- fats - 3%.
The most valuable part of dioecious nettle is its leaves. 100 g contains:
- 100-270 mg of ascorbic acid;
- 14-50 mg provitamin A;
- 41 mg iron;
- 8.2 mg manganese;
- 4.3 mg boron;
- 2.7 mg titanium;
- 0.03 mg nickel.
1 g of leaves contains 400 IU of vitamin K. The large discrepancy between the data on vitamins C and A is due to the very large area of the plant. Samples for research were collected in places with different soil composition.
In addition to vitamins and minerals, the leaves contain:
- chlorophyll up to 8%;
- tannins;
- sugar;
- organic acids;
- sitosterol;
- phytoncides;
- porphyrins;
- glycoside urticin;
- phenolic acids.
The rich chemical composition allows the herb to be used as a remedy in folk medicine. It is believed to help with a variety of ailments, including colds.
Medicinal properties of dioecious nettle
Due to its rich vitamin composition and medicinal properties, dioecious nettle has found application both in medicine and in cosmetology. In Russia, it has been used as a remedy for wound healing since the 16th century.
Leaves and roots are used for medicinal purposes. But the latter are much more difficult to prepare, although there is an opinion about their greater efficiency. Leaves are harvested on an industrial scale. For home use, they are also more convenient.
The plant is cut off entirely and dried for 2-3 hours. Then the leaves are cut off and dried in a ventilated room, spread out in a layer of 4 cm. The shelf life of dry raw materials is two years.

Stinging nettles work well for winter storage when frozen, salted, or canned
The use of dioecious nettle in medicine
In folk medicine, stinging nettle is very popular. The herb is used to treat many diseases:
- as a hemostatic for internal bleeding;
- for the treatment of polymenorrhea and endometriosis;
- to reduce too long periods;
- with rheumatism and joint diseases;
- for better wound healing;
- as a multivitamin preparation for colds;
- with diabetes to lower sugar levels.
Although all these diseases first of all require medical intervention, and not nettle broth. Internal bleeding is dangerous because they are invisible until the person loses consciousness. And inappropriate spotting in a woman can be a sign of uterine cancer. Here it is necessary to eliminate the cause, not suppress the symptom.
Any use of dioecious nettle in folk medicine is associated with the presence of a large amount of vitamin K in it, which accelerates blood clotting. Because of this property, uncontrolled intake of drugs from dioecious nettle will bring not only benefits, but also harm.
Official medicine is more careful about the medicinal properties of nettle. It is used in some preparations, but as an auxiliary ingredient:
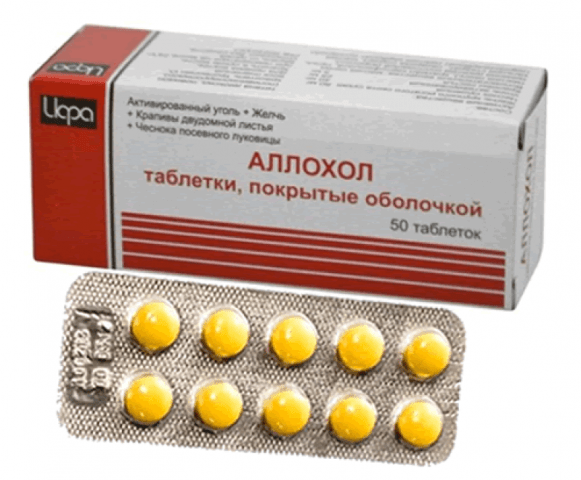
- Allochol, choleretic.
The tablets contain most of the dry bile - 80 mg and the least of the nettle - 5 mg.
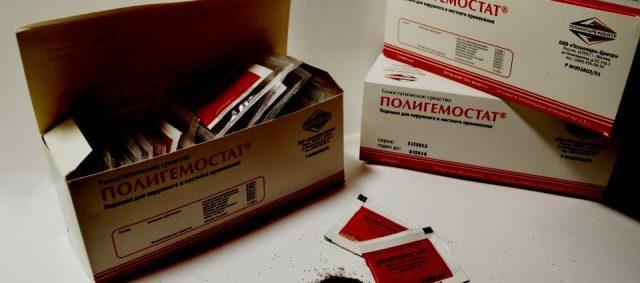
- Polyhemostat to stop external venous and capillary bleeding.
In a bag of Polyhemostat, weighing 2.5 g, the proportion of dry nettle extract is 25 mg.
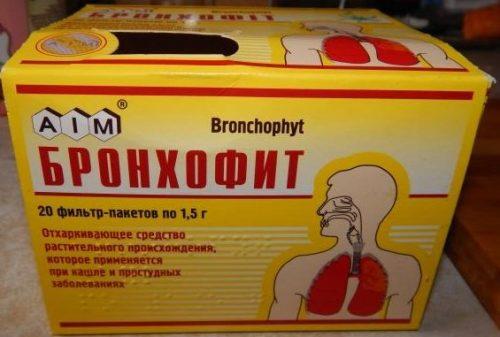
- Bronchofitis, herbal collection, which is used for diseases of the upper respiratory tract.
The Bronchophyte package contains only 8 g of nettle leaves.
The use of dioecious nettle is widespread in other areas as well.
Dosage forms
At home, you can prepare three types of medicinal preparations from dioecious nettle:
- infusion;
- broth;
- butter.
They are used not only in case of illness, but also for cosmetic procedures.

Nettle leaves can be brewed instead of tea
Decoction of dioecious nettle
For the broth, take 10 g of dry nettle leaves and a glass of boiling water. The herb is poured with water and kept on low heat for 15 minutes, not allowing it to boil. Insist 45 minutes. Filter the broth and add boiled water to 200 ml. Take 3-4 times a day, 100 ml.
Infusion of dioecious nettle
It differs from the broth in that more leaves are needed, and the cooking time is longer: 20 g of herbs per glass of boiling water and insist for two hours. Take 30 ml 3-4 times a day.
Stinging nettle oil
At home, nettle oil is obtained by cold or hot infusion. Any vegetable with a long oxidation period is taken as a basis:
- sunflower;
- sesame;
- olive;
- wheat germ;
- almond.
Methods for obtaining nettle oil differ in terms of preparation.
Cold method
With a cold infusion, the leaves of stinging nettle are folded into a jar, poured with oil and placed in a dark place. It takes a month to get the finished product. Shake the container daily to mix the contents better.
Hot method
To prepare the product using the hot infuse method, you will need a heat-resistant container. Grass is poured into it and oil is poured into it. Then they put it in a water bath and heat it up.
Heat the container for half an hour. The procedure is repeated for two more days.
Filtration and storage
The finished product is filtered to remove the leaves. A few drops of vitamin E are added to the oil. The latter needs 0.2 g per 100 ml of the drug. Store the finished product in the refrigerator. Shelf life is one year.

Stinging nettle seed oil is prepared in the same way as from the leaves
Rules for use for medicinal purposes
Decoctions and infusions are taken 30-60 minutes after meals. Better fresh. Store in the refrigerator for no more than two days. It is impossible to heat the finished preparations, and in case of colds, a warm drink is necessary.
But chilled infusions are suitable for external use. They are used for better healing of skin ulcers. You need to change the compress with nettle infusion every six hours.
And the main rule of using drugs from nettle is not to replace the medication prescribed by the doctor. Herbs give a good effect as ancillary, not basic.
Contraindications and side effects of dioecious nettle
Preparations from dioecious nettle should not be used for people with diseases of the cardiovascular system:
- hypertension;
- varicose veins;
- predisposition to thromboembolism;
- thrombophlebitis;
- other diseases that can cause blood clots to form in the vessels.
Nettle is contraindicated for people with individual intolerance.
Terms and rules for collecting dioecious nettle
Since dioecious nettle grows in all climatic zones of Russia, the timing of its collection in different regions differs. You need to focus on flowering. At this time, herbs accumulate the maximum amount of nutrients.
Stinging nettle blooms from May to late autumn. But in the southern regions, the grass usually dries up by June. Flowering there may begin in the second half of April. Therefore, it is necessary to focus on the appearance of inflorescences.

Separately dried flowers are a great addition to tea leaves
The stalks of dioecious nettle are mowed and dried in the shade in the air for about three hours. After that, the leaves and inflorescences are cut off. The latter can be used separately as an additive to tea. Then the raw material is dried and put into linen or paper packaging.
Do not use a plastic bag or glass jars to store dried stinging nettle. Condensation forms inside when the temperature drops. The shelf life of medicinal herbs is two years.
You cannot collect medicinal raw materials in environmentally dirty places:
- close to highways and railways;
- in landfills;
- near cattle burial grounds;
- not far from working or recently operating industrial enterprises;
- in places of storage of mineral fertilizers;
- neighborhoods of various construction projects.
Collect raw materials at a distance of more than 200 m from the unfavorable place.
The use of dioecious nettle in other areas
Young shoots are used to make vitamin soups. It is salted and fermented for use in winter. In the Caucasus, fresh leaves are added to salads and other dishes.
A decoction of stinging nettle is used to make hair shiny and silky. They rinse their head after washing.
The oil is used to improve the condition of the skin. It normalizes lipid metabolism, helps smooth out wrinkles on the face and prevents the formation of dandruff in the scalp.
Stinging nettle stimulates lactation and increases milk yield in cattle. Farmers often use it as a feed additive in the formulation of a ration for dairy cattle. Unscrupulous farmers feed their laying hens with this grass. Due to its high carotene content, stinging nettle contributes to the coloring of egg yolks in a bright orange color.
Conclusion
Stinging nettle helped out more than once in the past centuries in the spring, when food supplies were already coming to an end. She supplied people not only with nutrients, but also with a complex of vitamins. Today it is more commonly used as a medicinal plant, although it can diversify the spring menu.