Content
- 1 Place of corn in the crop rotation
- 2 Preparing corn kernels for planting
- 3 Sowing corn for grain
- 4 Density and seeding rate of grain corn
- 5 Fertilization of corn for grain
- 6 Stages of maize ripeness
- 7 Terms of harvesting corn for grain
- 8 Grain corn harvesting technology
- 9 Post-harvest corn processing
- 10 Storage of dry corn grain
- 11 Conclusion
The agricultural industry supplies the market with raw materials for food production. Corn is a high-yielding crop, the grains of which are used for food and technical purposes. Growing a plant is easy. The harvesting of corn for grain, the peculiarities of cultivation, drying, cleaning and storage are described below.
Place of corn in the crop rotation
The yield of a crop can fall, rise depending on the condition of the land, its vitamin content, moisture, and predecessors. Corn is a drought-resistant plant, but to obtain an average yield of 8 t / ha, during harvesting, 450 - 600 mm of precipitation is needed.
Corn yields little grain after drying out crops:
- sunflower;
- sorghum;
- sugar beet.
In arid regions, the recommended predecessors for grain corn are:
- winter wheat;
- legumes;
- potatoes;
- buckwheat;
- spring cereals;
- mustard;
- rape;
- coriander.
Thanks to modern technologies, corn can be grown as a monoculture for 2 - 3 consecutive years in one place, and in fertile soils with high rainfall - 4 - 5 seasons.
Preparing corn kernels for planting
The processing of the seed is carried out by special enterprises - corn-processing plants, where the grains, after passing through special technological processes, can be immediately planted in the ground. If it is not possible to hand over corn to the enterprise, then you will need to start preparing it yourself.
Grain required:
- calibrate;
- pickle.
Sizing - Separating seed by size, is done to separate large samples that might get stuck in the drill hole from the small corn. Further, the grains are subjected to solar or air-thermal heating for a week to accelerate germination.
The dressing is carried out to increase the protective properties of the seeds between sowing and germination. Grains that have absorbed water are alkaline, therefore they become a breeding ground for fungi in the ground. The fungicide creates a protective film that prevents disease from developing before germination.
To process seed, use:
- Insecticides.
- Fungicides.
- A mixture of the first and second kind.
Preparations and their recommended dosage:
- Thiram - with the active substance Thiram 4 l / t;
- TMTD - with the active ingredient Thiram 2 l / t;
- Aatiram - with the active substance Thiram 3 kg / t;
- TMTD98% Satek - with active ingredient Thiram 2 kg / t;
- Vitavax - with the active substance Carboxim + thyram Z l / t;
- Vitatiuram - with the active ingredient Carboxim + Thiram 2-3 l / t;
- Maxim Gold AP - with the active substance Fludioxonil + mefenoxam 1 l / t.
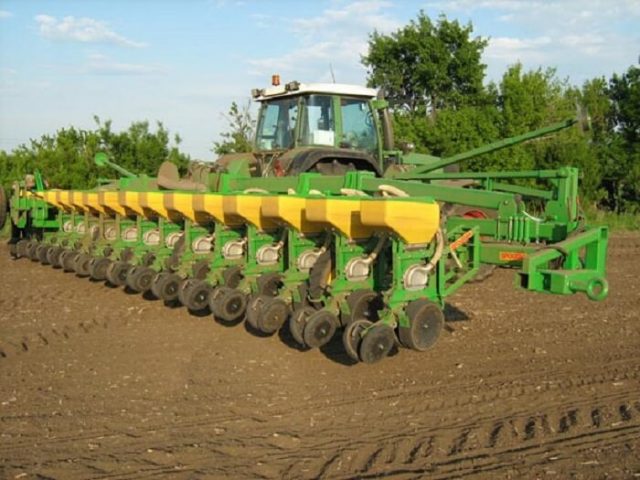
Sowing corn for grain
The term for planting seeds is determined by weather conditions, weediness of the field, early maturity of the variety and the temperature of the soil, which at a depth of 10 cm should warm up to 10 - 12 ° С. Cold-resistant crops are planted at a temperature of 8 - 10 ° C. Sowing of corn for grain is carried out in a dotted manner using tractors.
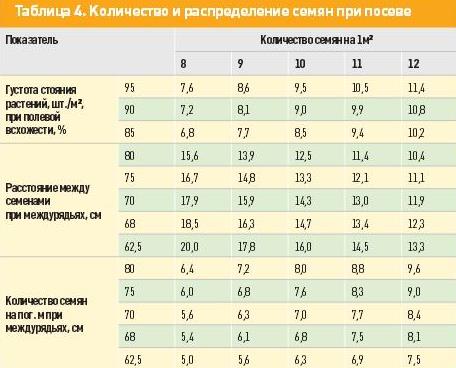
Density and seeding rate of grain corn
Sowing material is applied to the ground in early spring, most often from May 1 to May 15.The planting density per hectare depends on the fertility of the land, the amount of precipitation, germination and other parameters. Average rate for the standard technology of growing corn for grain:
- in arid regions: 20 - 25 thousand;
- in the steppe and forest-steppe zone: 30 - 40 thousand;
- with regular watering: 40 - 60 thousand;
- in the southern regions on irrigated soil: 50 - 55 thous.
The quantitative expression of the planting density - 15 - 22 pcs. for every 3 running meters, and in weight terms - 20 - 30 kg per hectare. If the field germination is poor, the rate is increased by 10-15%. Planting depth is 5 - 7 cm, in dry soil - 12 - 13 cm. Row spacing should be at least 70 cm.
Density of maize standing before harvest, expressed in thousands of plants per hectare.
Ripeness group | Steppe | Forest-steppe | Polesie |
FAO 100-200 | 65 — 70 | 80 — 85 | 90 — 95 |
FAO 200-300 | 60 — 65 | 75 — 80 | 85 — 90 |
FAO 300-400 | 55 — 60 | 70 — 75 | 80 — 85 |
FAO 400-500 | 50 — 55 | — | — |
Fertilization of corn for grain
Corn draws out 24 - 30 kg of nitrogen, 10 - 12 kg of phosphorus, 25 - 30 kg of potassium during the formation of 1 ton of grain, therefore it is necessary to replenish the elements or add them in case of a shortage. Top dressing application rate: N - 60 kg, P - 60 - 90 kg, K - 40 - 60 kg. Fertilizers for corn for grain are applied carefully, because the lack of nitrogen reduces the yield, and its excess delays ripening.
Before autumn plowing, rotted manure, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers and half of the nitrogen-containing substance are added. They are evenly distributed over the field with rotary spreaders, and for small field volumes - manually.
Pre-sowing top dressing of corn for grain has a good effect on growth, productivity. Superphosphate is introduced with seeds. It should be 3 - 5 cm deeper than the seed and 2 - 3 cm further, so as not to damage the shoots.
During primary and secondary processing of row spacings, the second half of nitrogen fertilizers are applied. To increase the protein content, foliar spraying with 30% urea should be done before harvesting.
Stages of maize ripeness
The grains ripen gradually, becoming harder at each stage. There are 5 stages of ripeness:
- dairy;
- early wax;
- late waxy;
- vitreous;
- complete.
Terms of harvesting corn for grain
The crop is ready for mowing when 65 - 70% of the ears have reached waxy maturity. There are two ways to harvest corn:
- On the cob with a percentage of moisture in the seeds not exceeding 40%.
- In grain with a moisture content of 32%.
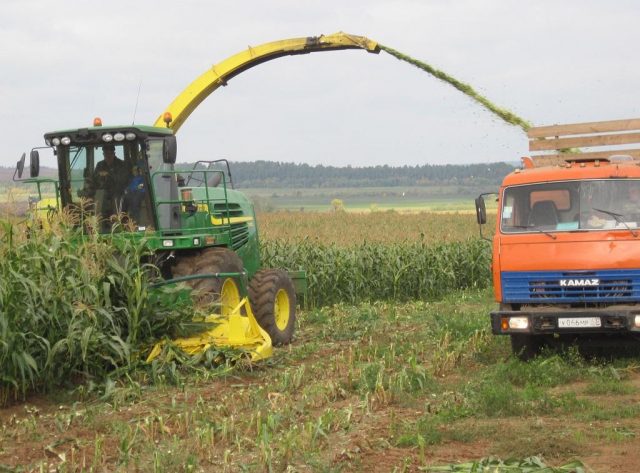
Corn harvesting is done by corn harvesters, or cob harvesters, as they are also called. For threshing, stream headers are used - special attachments for grain harvesting equipment, which, when harvesting, clean the cobs from seeds.
Grain corn harvesting technology
All types of combine harvesters with tangential or axial threshing devices are used. The quality of corn harvesting is influenced by two indicators:
- the scheme of the movement of equipment;
- level of quality.
The serviceability of the combine is checked before entering the field. The unloading equipment is also subjected to a thorough inspection.
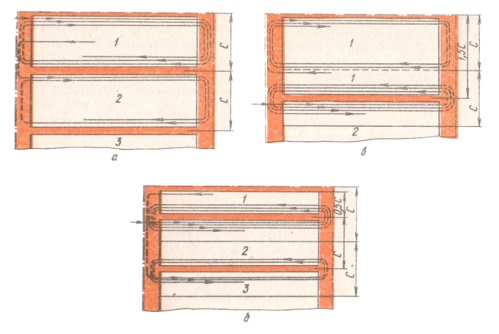
The scheme of movement of combines for collecting grain
It is recommended to harvest in the same direction in which it was planted. The field before the work of the combine is mowed around the perimeter, divided into corrals, starting from the butt row spacing. There are 2 ways to harvest grain corn:
- racing;
- circular.
The latter movement pattern is used in small fields.
Rutting method of harvesting:
1, 2, 3 - corrals, C - width.
The capacity of a combine harvester with a six-row corn head is 1.2 - 1.5 ha / h. The indicator depends on the time spent on shipment - when pouring onto a cart, the value is higher than when driving to the edge of the field.
How corn is harvested for grain can be seen in the video:
Indicator of the quality of the combine
Corn harvesting equipment does not always work well. You can assess the quality of harvesting crops by indicators:
- grain loss;
- cutting height;
- cleaning;
- the number of damaged ears.
To determine the quality of the work, you need to collect seeds and ears on an area of 10 square meters. m - 3 times.Knowing the yield of the crop, and after weighing the collected residues, determine the amount of losses as a percentage.
Post-harvest corn processing
Wet grains with garbage are not stored for a long time, therefore, before being sent to the hangar, they are cleaned of extraneous plant residues, and then dried. Coarse grains are not stored for long, therefore, moisture is allowed in them more than in seeds intended for planting.
Cleaning
To remove unwanted impurities, corn is passed through cleaning units. They are of 5 types according to the way they work:
- air;
- air sieve;
- separators;
- trier installations;
- pneumo-gravity tables.
In the units, the seeds undergo 3 degrees of cleaning:
- Primary: to eliminate weeds, leaf debris and other debris.
- Primary: to separate excess impurities.
- Secondary: for sorting by fractions.
Drying
Grain after harvesting is damp, contains many mineral, organic impurities, therefore it is poorly stored. Further processing of corn consists in dividing the seeds into categories according to moisture content. With a moisture content of 14 - 15%, they are sent to the storage immediately, with 15.5 - 17% - for drying and ventilation, with a high percentage of water - into the drying chamber.
Drying units are of several types:
- mine;
- columnar;
- bunker.
Drying plants by technological mode of operation:
- Direct-flow. They reduce grain moisture by 5 - 8%, but require material homogeneity.
- Recirculating. They do not require the same moisture content for corn, they dry better.
To make the moisture evaporate faster, use different drying modes:
- with preheating;
- with alternating heating-cooling;
- with mild temperature conditions.
Storage of dry corn grain
After harvesting, cleaning and drying, the seeds are sent to storage facilities. Corn for compound feed is stored with a grain moisture content of 15 - 16%, for food production - 14 - 15%. So that the seed does not deteriorate within a year, it is necessary to dry it up to 13 - 14%, more than a year - up to 12 - 13%.
The storage of grain corn for technical, food, fodder purposes is carried out in grain warehouses and bulk bunkers. The height of the heap is limited only by the storage roof, the convenience of quality control and maintenance. During storage, it is required to regularly clean the room.
Conclusion
Harvesting of corn for grain is carried out when it reaches wax maturity. The corn harvesters harvest the cobs or thresh them immediately. Harvesting is carried out at the stage of waxy maturity of the culture. Store grain in a dry, well-ventilated room after cleaning and drying.