Content
Currant bushes are susceptible to fungal diseases that affect the entire plant, reduce its immunity and winter hardiness. Plantations may die without timely treatment. In spring and early summer, the development of black and red currant bushes is closely monitored in order to prevent such an insidious disease as anthracnose.
How does the disease manifest
The onset of anthracnose infection of currants begins in the spring. The causative agents of currant anthracnose, overwintering on fallen leaves, are spread by insects and during the rain. Plants with the smallest mechanical damage are often affected.
Causes of the disease
This fungal disease is caused by several genera of marsupials. The disease affects the leaves and shoots of many plants, especially currants - red, white and black. The smallest spores, conidia, once on the plant, form mycelium in the tissues between the cells. The incubation period after exposure to spores causing anthracnose on black currants is approximately 2 weeks. Red currants get sick after a week. Having developed, the mycelium produces two generations of conidia - in May and July.
A favorable summer season for the development of the disease with frequent rains, when the humidity reaches 90%, and the air temperature is 22 0C. In such years, the widest spread of the disease is observed. In dry years, cases of damage are much less common. It is noticed that plants located on acidic soils, as well as with a lack of potassium and phosphorus, often suffer.
Infection routes
Anthracnose spores from diseased currant plants to healthy ones are transmitted in several ways:
- Spread by insects and mites;
- Air flows;
- The thickening of plantings of currant bushes and the remaining last year's leaves contribute to the disease.
Signs of infection
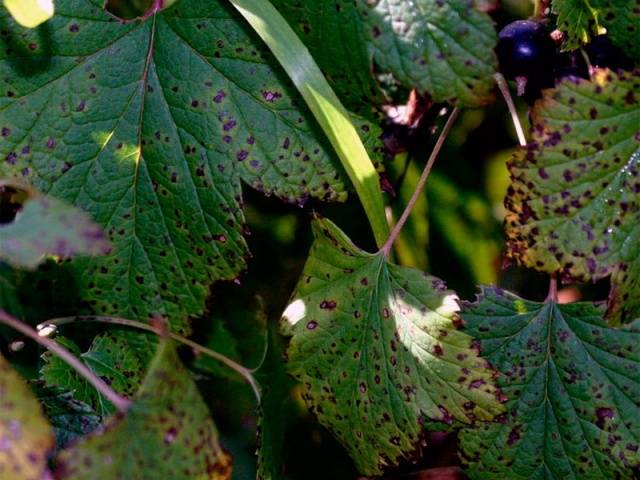
With anthracnose leaves, petioles, young branches, peduncles and, less often, berries are affected.
- A symptom of the onset of the disease is dark or light brown spots of a round shape, with a darker border, from 1 mm in size. Over time, the spots increase, merge into a large lesion area on the leaf blade, which becomes dry and falls off;
- Later, from the middle of summer, the second sporulation develops, visible on the black tubercles. When they are ripe and burst, they turn white. The disease through new pathogens captures a large area of the plant, it can continue until September;
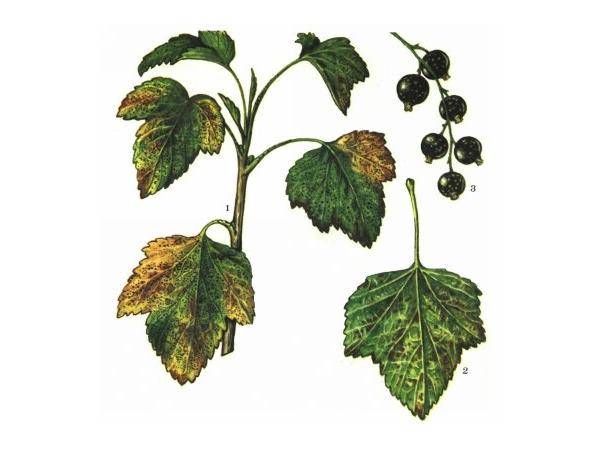
- Shoots, as well as petioles and stalks on red currants, are covered with dark depressed spots that prevent the free flow of nutrients;
- Later, in place of the spots on the shoots, cracks form. When wet weather returns, the shoots rot;
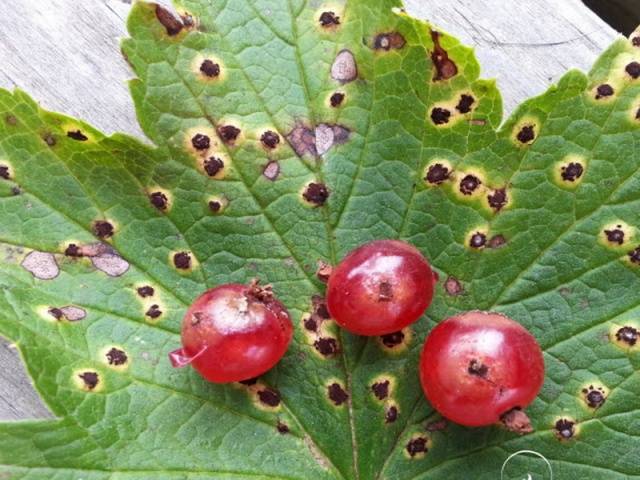
- If the disease spreads to the berries, it is recognized by small glossy dots of black or brown color with red edges;
- At the stage of leaf fall, young shoots wilt;
- In July, only new leaves may remain on the bush.
Consequences of the disease
It is possible to assess the condition of a diseased black currant bush in the middle of summer, especially if the temperature is kept below 19 degrees. On red currants, the disease manifests itself earlier - at the end of May, early June, if the temperature range ranges from 5 to 25 degrees. Leaves from bushes of red and white currants fall off almost immediately after the defeat.On black currants, brown and dried, twisted leaves sometimes remain until autumn. With unhindered development, up to 60% of the leaves fall off, the plant does not receive enough nutrients. The yield on the diseased bush is lost by 75%, the sugar content of the berries decreases, young shoots are not formed, up to 50% of the branches can die during the winter.
Anthracnose fungi overwinter on fallen leaves. If they are not removed from under the currant bushes, in the spring they produce new spores, and the bush becomes infected again. It happens that the disease goes away, but the plant weakens and without treatment and support may not recover.
Control measures
Knowing about the symptoms of the disease, gardeners use preventive measures to combat anthracnose on currants, carefully removing fallen leaves in the fall and digging up the soil under the bushes. Chemical treatment helps to destroy the pathogens of the currant disease. Each gardener chooses his own version from a range of drugs for the treatment of currant anthracnose. The bushes are sprayed in dry weather, when there is no wind, carefully processing each leaf.
Processing options
- Before bud break, 1 percent copper sulfate is used, cultivating the bushes and the soil under them;
- Captan, Phtalan (0.5%), Kuprozan (0.4%) or 3-4% Bordeaux liquid are used on unblown buds, before flowering or 10-20 days after harvest;
- Before flowering, the fungicide Topsin-M is also used in a mixture with drugs that stimulate immunity: Epin, Zircon;
- The currant is sprayed with Cineb or 1% Bordeaux liquid after flowering;
- If anthracnose is detected on currants during the ripening period of berries, treatment with microbiological preparations is carried out: Fitosporin-M, Gamair;
- After picking berries, currant bushes are re-treated with fungicides Fundazol, Previkur, Ridomil Gold or others.
Prophylaxis
Correct spacious planting and pruning of currant bushes, soil care, removal weeds, moderate watering, careful examination and regular preventive spraying will save plants from treatment for anthracnose disease.
Preventive treatments are carried out with drugs that protect plants from a wide range of fungal diseases and pests. Fungicides Cumulus DF, Tiovit Jet, Tsineb, Captan, solution 1% Bordeaux liquid is used after flowering and 15 days after picking the berries.
Noticing the first signs of anthracnose, the affected parts are removed so that the disease does not spread. In the fall, the fallen leaves are collected, and the soil is dug up.
From the experience of summer residents
Not all gardeners like to use chemicals, but they treat currant anthracnose with folk remedies every week.
- In March or February, depending on the region, the bushes are scalded with hot water along the sleeping buds, the temperature of which is not higher than 70 0C;
- Spraying the bushes with a solution of laundry soap is used for the treatment of currant anthracnose. Half the bar is grated and bred in a bucket of water, with a temperature of at least 22 0C;
- The currant bushes are treated with an infusion of 150 g of chopped garlic and 10 liters of warm water: the pungent smell scares away pests, and one of the ways of spreading currant anthracnose is interrupted;
- Iodine solution is used in the treatment of currant bushes. Its antiseptic property is equivalent to that of a fungicide. Iodine destroys microorganisms and provides preventive support to plants. For a working solution, 10 drops of iodine are diluted in 10 liters of water.
Top dressing
Plants with developed immunity are easier to treat.Currants are supported by complex feeds.
- For a 10-liter bucket of water, take 1 tbsp. spoon of potassium sulfate and ammonium nitrate, half a teaspoon of boric acid and 3 g of ferrous sulfate. Top dressing restores a depleted currant bush, helps to grow greenery and prevents leaf chlorosis;
- In the phase of ovary formation, top dressing with wood ash is prepared to improve the quality of the crop and increase the endurance of the currant. In a bucket of water, dissolve 200 g of ash, 1 bag of sodium humate, 2 tbsp. tablespoons of potassium sulfate and 1 tbsp. a spoonful of superphosphate;
- The use of "Immunocytofit" has a good effect: dilute 1 tablet of the drug in a bucket of water, add a solution of 1 tbsp. tablespoons of superphosphate and 2 tbsp. tablespoons of potassium sulfate.
When buying currants, you can choose varieties with high resistance to anthracnose:
- Black currant: Stakhanovka, Katun, Altai, Exhibition, Siberian daughter, Zoya, Belarusian sweet, Dove, Smart;
- Red currant: Faya fertile, Pervenets, Victoria, Chulkovskaya, Krasnaya Gollandskaya, London Market.
Disease caused by fungi can be defeated. Increased attention to the garden will bring a quality harvest.