Content
There is no mushroom picker who would not like to collect a whole basket of solid porcini mushrooms. Not knowing the exact proven places of their growth, you can focus on its preferences and the period of fruiting. Porcini mushrooms grow in a wide variety of places.
Where porcini mushrooms grow
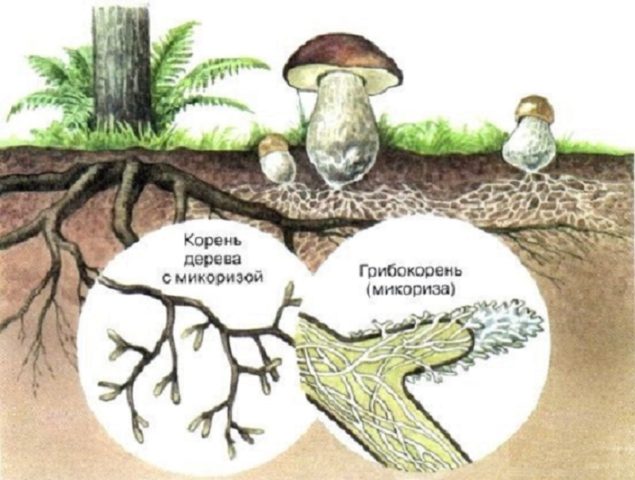
If you go into science, the porcini mushroom is not one species, there are about 18 varieties, and everyone has different preferences. Everyone creates a symbiosis (mycorrhiza) with specific types of trees, and of a strictly defined age. However, the finding of a symbiont tree does not at all mean that boletus is surely lurking under it. Soil composition, moisture level and ambient temperature are also important.
As befits noble representatives, boletus are very picky about conditions and do not grow anywhere. That is why avid mushroom pickers, who know the area well, are in no hurry to share their mushroom places, where porcini mushrooms bear fruit abundantly and annually.
In which forests do porcini mushrooms grow
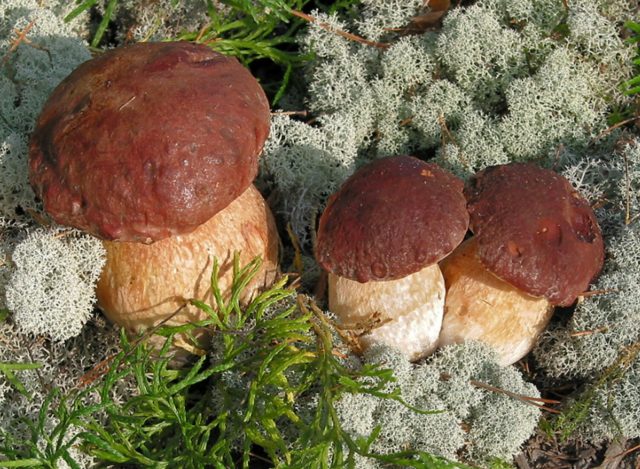
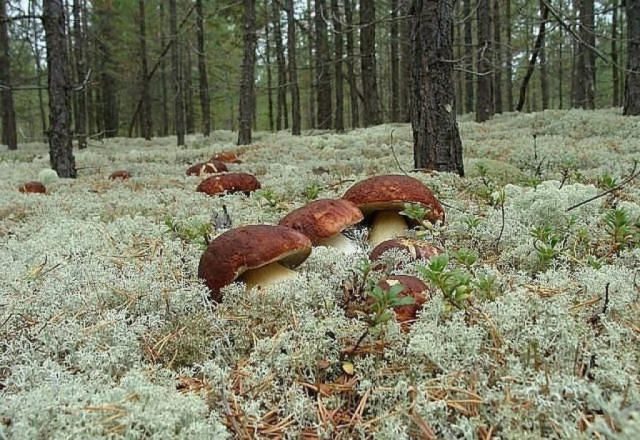
In the temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere, coniferous forests prevail. This is the most typical boletus landscape. Pine cep (Boletus pinophilus) usually settles in pine forests. It is distinguished by a reddish brown or chocolate cap and a thick puffy leg with a characteristic brownish mesh pattern. The fungus loves sandy soils and loams, never settles in lowlands and swamps. In mountainous areas, he prefers higher places.
Typical growing areas:
- sphagnum or lichen clearings;
- edges of glades and glades;
- forest roadsides.
A similar species can be found in spruce forests - the spruce white mushroom (Boletus edulis). He is a typical representative of the genus and is often referred to as common. The color of the cap varies from light to dark brown. Its growing conditions are identical to the previous species: its favorite places are well-lit dry areas with a dense litter of lichens and mosses. Spruce boletus also grows in old fir and spruce-fir forests.
Porcini mushrooms also grow in deciduous forests, which also occupy a considerable area, especially in the southern regions. The most unpretentious and widespread is the birch cep (Boletus betulicola), which is popularly called the spikelet. The first boletus appear in the forest when rye begins to spike. They can be found in almost any birch forest, especially along the edge of open areas and on the edges.
To increase the likelihood of finding a spikelet, you need to know two signs:
- Porcini mushrooms grow in a birch forest, where there are tussocks of whitebeard grass.
- Chanterelles and red fly agaric mushrooms are neighbors of the birch boletus.
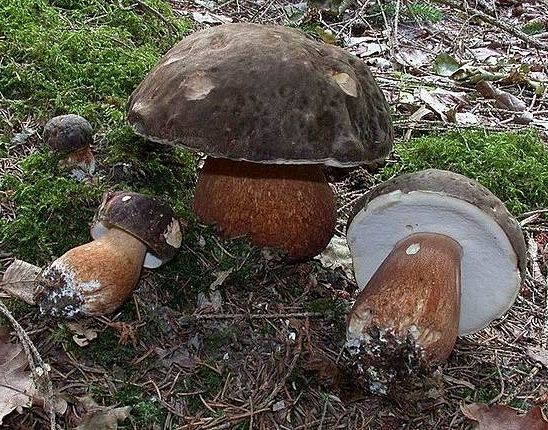
Porcini mushrooms, called bronze boletus (Boletus aereus), are collected in oak forests. They have a dark, in some cases almost black color of the cap with a whitish coating that resembles mold. Mushrooms grow in warm climates and are rare in mountainous areas. The most widespread are found in southwestern Europe, as well as in North America.
Many mycologists note the greatest concentration of porcini mushrooms in mixed forests. This is due to the presence of several symbionts at once, which allows different species to grow on the same territory. The undergrowth plays an important role. The massive growth of boletus is associated with the presence of birch, because the variety that creates mycorrhiza with it is the most common of all.
Where porcini mushrooms grow in Russia
The growing area of the porcini mushroom on the world map covers all continents, excluding Australia and the polar regions of Antarctica. In Russia, it is distributed from the Murmansk region to the Caucasus Mountains, from the western borders to the Chukotka Peninsula. However, boletus grows not everywhere. For example, in the tundra and forest-tundra it is extremely rare, but in the northern taiga it bears fruit abundantly. From the western regions to Eastern Siberia, the population of porcini mushrooms is gradually decreasing, in the Far East boletus mushrooms are not uncommon. In forest-steppe conditions, they are rare, in the steppe zone they do not grow.
Under what trees do porcini mushrooms grow
Boletus creates mycorrhiza with trees such as:
- spruce;
- Pine;
- fir;
- oak;
- Birch tree.
Some experts claim that porcini mushrooms grow in elm and elm forests. There are known cases of birch, pine and spruce varieties found there. But many mycologists talk about the difficulties of forming a symbiotic relationship with the elm due to the specificity of biological processes in the tree.
Speaking about the preferences of boletus, one cannot ignore the age of the forest. The older and more virgin the area, the more likely they are to be found. They grow under trees 20-50 years old and older, because the formation and development of mycelium in these representatives of the genus Boletus takes more than a dozen years.
Where do porcini mushrooms grow?
In the lowland areas, boletus are more common than in mountainous areas. They prefer well-drained, non-waterlogged soils:
- sandstones;
- sandy loam;
- loams.
Boletus practically do not grow in peat bogs and swampy areas. They like lighted areas where trees are rarely located, but it happens that they bear fruit abundantly in the shade under the dense crowns of conifers. Interestingly, in a harvest year, illumination does not play a significant role, but in rainy and cold summers, boletus mushrooms appear only at the borders of the forest, where the land is drier and the soil warms up better. In hot weather, fruiting bodies grow in the grass under bushes, in the shade of trees. You need to look for porcini mushrooms in the forest in places where there is a litter of moss (cuckoo flax, sphagnum, lichen) and lichens.
When to pick porcini mushrooms
The fruiting time of boletus mushrooms depends on the climate. In the northern temperate zone, porcini mushrooms are harvested from mid-June to late September. There are cases when they were found at the end of spring, but this is rather an exception to the rule. In warm regions, the time for harvesting porcini mushrooms stretches to October.
In what month is the porcini mushroom harvested
The most massive growth is observed in the second half of August. Boletus grow singly and in groups, sometimes forming circles, popularly called "witch's rings".
At what temperature do porcini mushrooms grow
Optimum temperature for the development and growth of the fruiting body:
- in July-August - 15-18 ° C;
- in September - 8-10 ° C.
When the temperature rises to 20 ° C, the growth of mycelium and the formation of fruiting bodies slows down. Sudden changes in temperature at night and excessive humidity are not good for the boletus. The most favorable weather conditions for him are considered to be moderately warm weather with short-term thunderstorms and night fogs.
Other types are peculiar indicators of the appearance of this representative:
- spruce and pine boletus appears simultaneously with green tea (Tricholoma equestre);
- the birch form begins to grow with the appearance of common chanterelles (Cantharellus cibarius);
- it makes sense to look in the oak groves when the first green russules (Russula aeruginea) emerge.
How long does the white mushroom grow
The growth rate of porcini mushrooms directly depends on weather conditions. Air humidity should be within 60%. If, after prolonged inclement weather, drought comes abruptly, the species stops growing, even if the soil is sufficiently well moistened. At low humidity, the fruit body dries quickly, since it is not protected from evaporation.
Porcini mushrooms grow most intensively after rain. This is especially noticeable in young specimens in the first three hours after heavy, but short-term precipitation. Already on the 4-5th day, the weight of the fruiting body can reach 180 g. On average, it takes a week for the boletus to reach an adult state.
Growth is also affected by pest larvae. If they crawl upwards from the bottom of the stem, development does not stop; in case of damage to the cap, the boletus stops growing. According to the observations of mycologists, a nearby growing fungus, not affected by insects, begins to develop much faster than its sick fellow. In some cases, egg clutches are destroyed by proteins or slugs, then the fruit can grow to a very impressive size.
The life of the porcini mushroom is short - only 12-14 days. At first, the stem stops growing, after 2-3 days, the cap also stops. Rapid aging begins as soon as the spores mature.
How to find a porcini mushroom in the forest
Summarizing the above, we can reduce the nuances of the growth of whites to the following points:
- Birches, fir trees, pines, fir trees, oaks should grow in the forest.
- The trees are at least 20-50 years old.
- The terrain is dry enough, not swampy.
- The soil is loamy, sandy or sandy loam.
- The forest litter is represented by mosses and lichens, and grass bumps are present.
- Porcini mushrooms are photophilous, grow on the edges and in woodlands, preferring higher elevations.
How to pick porcini mushrooms correctly
The collection is safe only in ecologically clean places, away from the roadway and industrial facilities. It is better to leave suspicious specimens in the forest, because one single fruit can cause poisoning or damage to the entire batch of blanks.
Fruit bodies are carefully cut with a knife at the base, inspected for worminess and placed in baskets. Can be collected in plastic bags, white ones do not wrinkle as much as russula.
Most mushroom pickers have heard from childhood that the fruits cannot be uprooted or twisted. According to many, this attitude towards forest gifts can damage the mycelium. In fact, the fruiting body is nothing more than a kind of "stand" for the ripening of spores, the main part is located underground. When a small amount of mycelium filaments breaks in the place where the fruiting body was torn off, the mycelium does not suffer much. The threads are in the billions, and the wounds heal quickly.
Conclusion
Having learned when and where porcini mushrooms grow, you can safely go to the forest. Considering all the nuances and preferences of these capricious forest dwellers, you can be sure that the basket will not remain empty. And even if the harvest is modest, a walk in the forest is a pleasure in itself.