Content
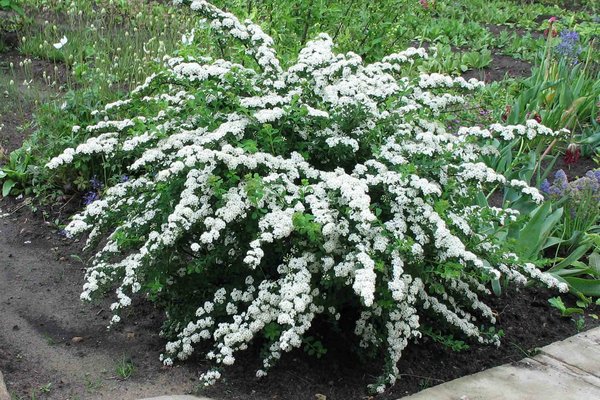
Spirea Snowmound belongs to the genus of deciduous, ornamental shrubs of the Pink family. The name of the plant is based on the ancient Greek word "speira", which means "bend". The shrub was named so because its shoots are very elastic - they bend easily, but then quickly take their original position without forming fractures. The main advantage of spirea is its ease of care. In addition, the flowering of this variety is considered the most spectacular among all the spirits that bloom in spring.
Features of planting and caring for this garden culture, as well as a photo of Snowmound's spirea are presented in the sections below.
Description of spirea Snowmound
Spirea Snowmound is a small spreading shrub, the height of which does not exceed 1.5 m. The diameter of the plant is 1-1.5 m. This garden culture does not grow very quickly - the average annual growth of the shrub reaches 20 cm under favorable climatic conditions and proper care.
The skeletal branches of the Snowmound spirea are arranged vertically, however, the ends of the shoots sag, as a result of which a kind of arc is formed. The variety blooms profusely. Flowering dates are early-mid June. The flowers of the Snowmound spirea are small - about 8 mm in diameter. The petals are white.
The variety blooms on last year's shoots, so the plant is cut off immediately after flowering. To do this, remove both faded branches and dried or damaged shoots. If the shrub grows strongly, its shape and height are corrected.
Spirea Snowmound leaves are oval. Above, the leaf plate is dark green, on the back side it is pale, greenish-blue.
This variety is resistant to low temperatures and undemanding to air quality, which allows you to grow shrubs not only in the garden area, but also in the city, in conditions of increased environmental pollution. The composition and quality of the soil also does not really matter, however, Snowmound spiraea develops best on loose, moderately moist soils. The plant does not tolerate stagnant water well.
Resistance to pests and diseases is high. The variety rarely gets sick and practically does not attract insects.
Spirea Snowmound in landscape design
In landscape design, the variety is used for both specimen and group plantings. Snowmound's spirea looks very impressive as a hedge. When planting a clump of spirits of different varieties with early flowering periods, this will allow you to stretch the flowering of the flower bed.
Combinations of spirea with the following garden crops have proven themselves well:
- astilbe;
- lilac;
- lilies of the valley;
- primroses.
You can also plant perennial ground cover plants around the shrub, such as periwinkle and painted ash.
Planting and caring for Snowmound spirea
The Snowmound variety is usually planted in well-lit areas, but planting in partial shade is also possible. Heavy shading negatively affects the growth of the shrub.
Preparation of planting material and site
Before planting seedlings in open ground, it is necessary to carefully select the planting material. It is better not to plant weak and underdeveloped plants. It is also advisable to cut roots that are too long.In this case, the cut must be even, for which it is necessary to use only sharp tools. When pruning with blunt scissors or a knife, fractures may form, which negatively affect the further development of the bush.
Landing rules
Planting of plants is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- The seedlings are watered abundantly and removed from the container.
- If the earthen lump is too dry, the planting material is soaked for an hour in a bucket of water.
- Then the plant is lowered into the planting hole, spreading the roots.
- Sprinkle the hole with soil mixture so that the root collar of the seedling is flush with the soil surface.
- After that, the trunk circle is lightly tamped and watered moderately.
Watering and feeding
Water the bushes in moderation. In dry weather, the frequency of watering is 2 times a month, while no more than 1 bucket of water is used for 1 bush. Young seedlings are watered a little more often.
Planting is fed with complex mineral fertilizers.
Pruning
The Snowmound spirea is usually cut off in March. For this, the shoot is shortened to large buds. It is recommended to remove small and weak branches completely - intensive pruning stimulates the shoots of the shrub.
You can learn more about the features of trimming the spirea from the video below:
Preparing for winter
Spirea Snowmound is a frost-resistant variety, however, young seedlings must be covered for the winter. For this, dry leaves and peat are used. The optimal cover layer is 8-10 cm.
Reproduction
The Snowmouth variety is propagated by the following vegetative methods:
- cuttings;
- layering;
- in small deeds.
The most effective is the cultivation of Snowmound spirea by means of cuttings - with this method of reproduction, more than 70% of the planting material takes root. Cuttings are harvested in early June. The preparation procedure is as follows:
- The most direct annual shoot is chosen on the bush and cut off at the base.
- The cut off branch is divided into several parts so that there are at least 5 leaves on each cutting.
- At each cut, the bottom sheet is removed along with the petiole. The remaining leaves are cut in half.
- The planting material is immersed in the Epin solution for 10-12 hours. The recommended dosage is 1 ml per 2 liters of water.
- Then the cuttings are taken out and the lower node is treated with a growth stimulator. You can use the drug "Kornevin" for this.
- After that, the planting material is planted in a container with wet sand. The plants are deepened at an angle of 45º.
- The cuttings are covered with plastic wrap or glass to create greenhouse conditions. As the plants grow, they are regularly moisturized.
- With the onset of cold weather, cuttings are dropped in the garden area and covered with dry leaves. Above is installed protection in the form of an inverted box.
- The following spring, the plants are opened and transplanted to a permanent location.
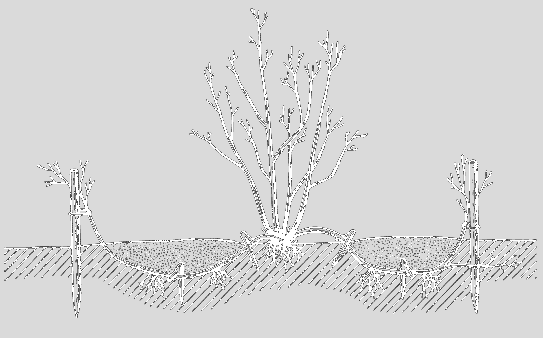
Spirea propagation by layering occurs according to the following scheme:
- In the spring, one of the lower shoots is bent to the ground.
- The end of the branch is buried and fixed with a heavy object or staple. Water the layers in the same way as the main part of the shrub.
- In the fall, it is separated from the mother bush and planted.
You can share the spirea both in spring and autumn. The recommended time for the procedure is late August-early September.
Division Algorithm:
- A spirea bush is dug out, focusing on the diameter of the crown.
- For 1-2 hours, the plant is lowered into a basin of water to soften the soil on the roots of the bush.
- The damp earth is washed off, after which it is necessary to straighten the root system of the bush.
- The rhizome is cut into 2-3 pieces with a knife or secateurs. Each division must have at least 2 strong shoots.
- The dividing procedure is completed by planting the resulting parts in the holes and abundant watering.
Diseases and pests
Spirea Snowmound practically does not get sick. The following insects can be distinguished as the main pests:
- sawfly;
- aphid;
- haplitsa.
It is not difficult to get rid of them - it is enough to spray the bushes with industrial or natural insecticides. The drug "Pirimor" has proven itself well.
Conclusion
Spirea Snowmound is one of the most popular varieties of the Rose family. The prevalence of the plant is explained by its unpretentiousness and frost resistance, as well as its high decorative qualities. The shrub can be grown both singly and as part of flower groups.